DNA Replication : The Introduction
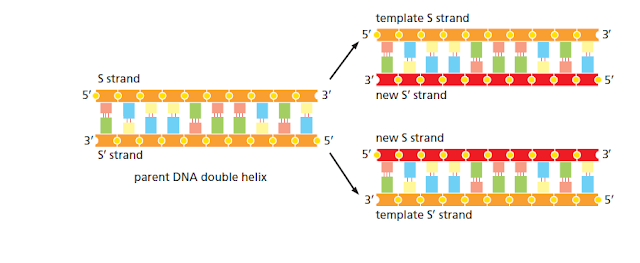
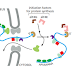
DNA templating is the mechanism the cell uses to copy the nucleotide sequence of one DNA strand into a complementary DNA sequence This process requires the separation of the DNA helix into two template strands, and entails the recognition of each nucleotide in the DNA template strands by a free (unpolymerized) complementary nucleotide.
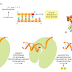
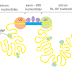
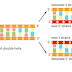
During DNA replication inside a cell, each of the two original DNA strands serves as a template for the formation of an entire new strand. Because each of the two daughters of a dividing cell inherits a new DNA double helix containing one original and one new strand (Figure 5–5), the DNA double helix is said to be replicated “semiconservatively.” How is this feat accomplished?
In all cells, DNA sequences are maintained and replicated with high fidelity. The mutation rate, approximately one nucleotide change per 1010 nucleotides each time the DNA is replicated, is roughly the same for organisms as different as bacteria and humans. Because of this remarkable accuracy, the sequence of the human genome (approximately 3.2 × 109 nucleotide pairs) is unchanged or changed by only a few nucleotides each time a typical human cell divides. This allows most humans to pass accurate genetic instructions from one generation to the next, and also to avoid the changes in somatic cells that lead to cancer.
.png)




0 komentar: